Resolving SMTP relay service email issues in Microsoft Exchange and Google Workspace
This article describes the email delivery issues organizations using a SMTP relay service in their Microsoft Exchange or Google Workspace email process may experience. It also explains how to resolve these issues.
Issue
Organizations using a SMTP relay service in their email process may experience the following email delivery issues:
- Incoming messages received from trusted senders are being flagged as false-positives by Microsoft, Google, or third-party service providers.
- Incoming messages received from trusted senders are being placed in the "Junk" folder.
- Warnings about phishing or spam appear in messages received from trusted senders.
- Incorrect behaviour of custom mail flow rules or sender whitelisting.
- Authentication of sender through Sender Policy Framework (SPF) “failed” or “soft failed“ because of an unauthorized third-party IP address detected in the mail flow.
- DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM) verification failed because modification of the email content was detected.
IMPORTANT Symptoms could occur intermittently, meaning some messages may be delivered properly while others from the same sender may be blocked.
Why does this issue occur?
As demonstrated in the schema below, when an organization has integrated an SMTP relay service, such as Barracuda or Proofpoint, into their email delivery process, an email sent to the organization from an outside entity will be received by the SMTP relay server first. The SMTP server may make modifications to the email, like adding its own information in the header or including security warnings in the message body or title, before it sends it on to the Microsoft Exchange or Google Workspace server.
Upon receiving the email, the mail server will identify that the sender of the email, the relay server, has a different IP address than the original sender and will most likely determine that the sender is unauthorized.
In addition, the mail server can identify any modifications that have been made to the email by the SMTP relay server via the DKIM signature. The DKIM signature may show that the original email content does not match the final email content.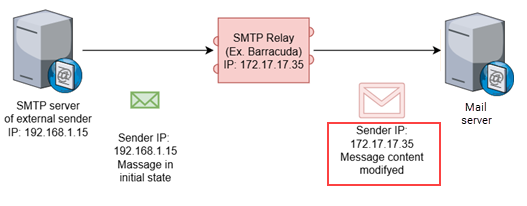
The insecure delivery flow and the modification of the original email would cause the mail server and any anti-phishing services enabled in the environment to identify the email as a possible threat and block delivery.
Such behaviour is very similar to the security breach known as a man-in-the-middle attack. In this attack, the bad actor obtains access to a company's communication channel and changes messages between the sender and recipient in order to create harm for the company.
Enhanced Filtering for Connectors in Microsoft Exchange
To make using SMTP relay based services with Microsoft Exchange secure and avoid email deliverability issues, you should enable Enhanced Filtering for Connectors in Microsoft Exchange.
Setting up a connector with Enhanced Filtering will authorize your SMTP relay service to translate the email message it receives so Microsoft Exchange can identify and authenticate the original sender. This improves validation of the DKIM signature by providing Microsoft Exchange access to the initial state of the email message when possible. Email messages will be filtered based on their actual content and status of the initial sender.
This schema illustrates the result of enabling Enhanced Filtering for Connectors in Microsoft Exchange when an SMTP relay service is being used for email delivery. The SMTP relay service has translated the email message so the Exchange server can identify the original sender's IP address and view original email.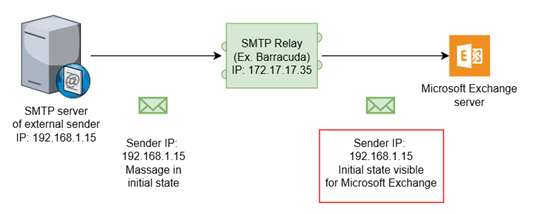
For information about enabling the connector, see the Microsoft article Enhanced Filtering for Connectors in Exchange Online.
Set up an inbound mail gateway for Gmail
To make using SMTP relay based services with Gmail secure and avoid email deliverability issues, you should set up Gmail to accept messages it gets from inbound mail gateways.
Setting up an inbound mail gateway will authorize your SMTP relay service to translate the email message it receives so Gmail can identify and authenticate the original sender. This improves SPF validation by instructing Gmail where to find the original sender of the email. Email messages will be filtered based on their actual content and the status of the original sender.
This schema illustrates the result of setting up an inbound mail gateway when an SMTP relay service is being used for email delivery. The SMTP relay service has translated the email message so the Gmail server can identify the original sender's IP address and view original email.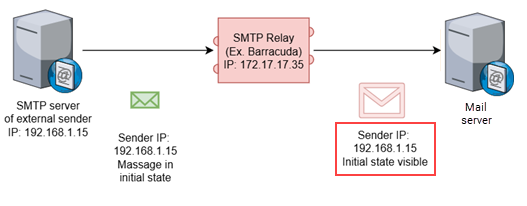
For information about setting up an inbound mail gateway, see the Google Workspace article Set up an inbound mail gateway.
Benefits of configuring the mail server when using SMTP relay-based services
The following summarizes the benefits of configuring Enhanced Filtering for Connectors in Microsoft Exchange or setting up an inbound mail gateway in Gmail when using SMTP relay-based services:
- The mail server remains secure and protected from man-in-the-middle attacks.
- Email flow and all anti-phishing protection services integrated with the mail server function properly.
- Improved deliverability of messages from external senders by reducing false positives in email filtering.
- Enhanced visibility and information within mail server tools for investigating potential threats.
| Revision | Date |
|---|---|
| Original release. | 2/18/25 |
| Added Google content | 7/14/25 |